A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger that is replicated and distributed throughout the network of computer systems on the blockchain, which means every computer (node) in the network has a copy of the transaction that takes place. These nodes could comprise any computer system, such as servers, personal computers, and even mobile phones.
This system is also known as peer-to-peer technology because each node being part of the blockchain network approves each transaction and receives a copy of the transaction details.
The goal of the blockchain is to record and distribute digital information, not to manipulate it. In this way, the blockchain is the basis for recording immutable ledgers or transactions that cannot be modified, deleted, or destroyed, adding to reliability and robustness.
Why is it called a blockchain?
Developers in the early days wanted to introduce a computationally viable solution for time-stamping digital documents so that they couldn’t be dated or tampered with. They developed a system for storing time-stamped documents using the concept of a chain of cryptographically protected blocks.
Merkle tree was used to create a “chain of protected blocks”. A series of records is saved, and each record is linked to the previous record. The latest record for this chain contains a history of the entire chain. However, this technology remained unused.
Fig. 1 Merkle Trees
The terms block and chain were used separately in Satoshi Nakamoto’s original work, but by 2016, they became popular as one term, Blockchain
The name “blockchain” comes from how it works and how it stores data. That is, the information is packed into blocks that are linked to other blocks of similar information to form a chain. A series of records is saved, and each record is linked to the previous record. The latest record for this chain contains a history of the entire chain.
Satoshi uniquely improves the design to add blocks to the original chain without the need for signatures by trusted parties. The modified tree contains a secure history of data exchanges.
Satoshi was responsible for most of the work done, and he was active in making changes and publishing technical information on Bitcoin. Before vanishing from the face of the earth, Satoshi handed over control of the Bitcoin core codebase for public use. The identity of this person has not been revealed.

Fig. 2 Statue of anonymous Bitcoin founder unveiled in Hungary
Bitcoin and blockchain were described as a “peer-to-peer electronic cash system”. It contains a hash code (00001 #, 00002 #, etc.) that is interlinked with each other. Therefore, each transaction is associated with both the previous transaction and the next transaction.
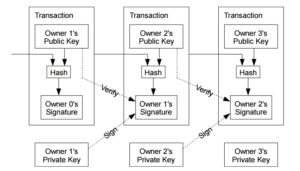
Fig. 3 Peer-to-peer electronic cash system
It utilizes a peer-to-peer network for time-stamping and verifying each exchange. It could be managed autonomously without requiring a central authority. These improvements were so beneficial that make blockchains the backbone of cryptocurrencies. Today, the design serves as the public ledger for all transactions in the cryptocurrency space.
It is this digital transaction chain that makes it very difficult to alter because the changes affect the sequence.
The fact that all payment transactions need to be “approved” by all computers registered on the network also protects the chain from external interference.
Why is blockchain different from regular banking?
Payments made through banks and other financial institutions are subject to regulatory requirements and government intervention, but blockchains are completely autonomous and independent payment systems.
The funding process is a time-consuming task, as the funds received from commercial banks are short-lived and require many checks on the part of the bank. Banks can set difficult conditions for making loans.
The power over your own money is held by banks, which are centralized in nature. They act as middlemen in the transaction process and can easily manipulate the whole system and process.
However, blockchain for the most part is decentralized in nature and thus does not depend on banks. This allows users to make payments without the potential block from payment providers, i.e. a bank.
Banks act as central authority that doesn’t provide options for transactions. Users can’t choose the currencies on their own for trading. So, if the banks fail or publish new laws regarding currencies, it can affect the general population that we observed during demonetization in India.
However, using blockchain users can choose when and how much to pay in cryptocurrencies and use different cryptocurrencies to pay for goods, services, and even property.
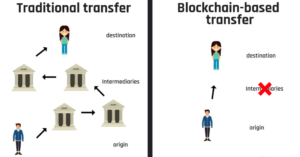
Fig. 4 Traditional vs Blockchain approach
Some of the existing cryptocurrencies on the market (currently over 5550) are more compatible than other cryptocurrencies for certain payments. For example, one of the most widely used cryptocurrencies, Ripple XRP competes with SWIFT, the global network of interbank transfers.
Bitcoin is still the most popular cryptocurrency in everyday user transactions, but cryptocurrencies are now being evaluated just like traditional currencies, such as investing and buying assets like Ethereum. There are many currencies that have proven to be popular with users for a variety of purposes.
Is Blockchain safe?
Despite some murky predictions about the future of Bitcoin and Blockchain technology, both have proven to be easy and secure ways to make quick and inexpensive transactions.
This Chain technology, in which each payment is made, refers to all computers on the network to approve the previous and subsequent payments at the time and has been proven to be highly secure and possibly the safest way to make payments online.
Users can also remain anonymous; cryptocurrencies are stored in anonymous online “wallets” where the user’s identity is not known. This raises concerns due to law enforcement where cryptocurrencies have attracted cybercrime to the system simply because it is a secure and anonymous system.
However, it is technically difficult to change payment records once they have been recorded without attracting much attention. Blockchain is considered one of the most secure payment systems.
What is the degree of security blockchain offers?
A blockchain contains a chain of blocks that record transactions. Each block has a connection between the subsequent block and the previous block. As a result, it is virtually impossible for anyone to tamper with a record.
Blockchain technology creates data structures with unique security qualities. It is based on cryptographic, decentralized, and consensus principles that guarantee transaction trust.
In the future, there are concerns that quantum computers could hack into the system and possibly alter payments as they are made, but before they are recorded in the Blockchain ledger.
Knowing this, it is likely that the technology itself will evolve to prevent this, and it is estimated that the possibility of a Blockchain being hacked by a quantum computer will take at least ten years to become a reality. For example, Bitcoin uses two encryption features: SHA-256 for hashes and ECDSA for public/private keys.
Quantum computers are primarily a threat to attacks on public/private key systems. Within Bitcoin, public/private keys are only exposed during a transaction. This means that Bitcoin is at risk in the process of creating a transaction and adding it to the blockchain. Of course, this requires a very fast quantum computer and is unlikely to be readily available.
On the other hand, many other systems are all based on pre-quantum computing encryption and are at risk. In 2019, Google used the quantum computer Sycamore to solve a problem that took less than three minutes to solve on a quantum computer which would normally take more than 10,000 years to solve on a current supercomputer.

–
Fig. 5 Quantum Computers
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor the Blockchain is also under development, although there are concerns about its use. However, AI will eventually be developed to create algorithms that can work with encrypted data. This will allow the technology to recognize fraudulent financial transactions that require investigation. Currently, such investigations are extremely time-consuming because they involve large amounts of complex data processed by humans.
Blockchain vs. traditional payment methods
One of the main attractions of cryptocurrency and Blockchain payments to users is the fact that payments can be considered almost instantaneous, compared to traditional banking systems.
Crypto and blockchain payments are estimated to be around ten times faster than traditional bank payments and with cryptocurrencies like Ripple XRP positioned to compete with the system SWIFT banks, it is likely that technology will become more efficient and secure as technology and user adoption rates increase.
Challenges currently faced by blockchain
Many still doubt that cryptocurrencies and Blockchain will prove to be the new universal banking method. There are some concerns raised:-
- Prominent economist, Nouriel Roubini points out that Blockchain “lacks the kind of universal and common core protocols that make the Internet globally accessible (TCP-IP, HTML, etc.)”.
- Other commentators cite that Blockchain is not indestructible, or that the technology’s anonymity is actually a downside. It is now possible to track cryptocurrency movements online. Some companies specialize in this for law enforcement purposes, so complete anonymity may not be possible. Similar to how cookies track user interactions online and reveal behavioral patterns, interests, and associates, payment patterns can reveal potentially sensitive information about identity or location.
- One of the main disadvantages of Blockchain is that it is not very energy efficient, as generating each new block of data after each transaction consumes energy. Some climate activists and politicians claim this reason alone in the current climate debate. According to them, this technology may prove unsustainable.
- Another disadvantage of the Blockchain is that the process of downloading the accumulated Blockchain data from the platform consumes time and uses up storage capacity on devices. Also, as more payments are made, the size of the data chain increases. It further increases the processing time of the data blocks.
- Some critics say that Blockchain operates in the same way other systems do. This is because established systems like Visa and Mastercard already have millions of users, and the comparatively small number of people using cryptocurrencies and Blockchain worldwide means that they cannot compete with the current global payment systems. However, rating data show that the number of daily use transactions for cryptocurrencies and Blockchain is increasing by millions every year, and as the value of cryptocurrencies continues to rise, user numbers are likely to grow.
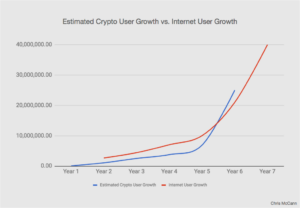
Fig. 6 Growth of Crypto Users
Compared to banking systems currently in place, Blockchain may still be in its infancy. The technology was only unveiled in 2008, but cryptocurrencies and Blockchain have so far defied the doubters to provide a new, secure, and efficient way of handling digital payments globally, and without the need for regulation or government intrusion, paving the way for an innovative but decentralized peer-to-peer payments system that anyone with some computer skills can use.










